43 gas laws calculations worksheet
Practice calculating pressure, volume, temperature, and moles of gas using the ideal gas equation. ... Using the ideal gas law to calculate a change in volume. Gas mixtures and partial pressures. Dalton's law of partial pressure. Worked example: Calculating partial pressures.
View 5.04 Assignment Gas Laws Calculations.docx from COM MISC at Mceachern High School. CVA Chemistry Module 5 5.04 Gas Calculations Worksheet Complete the calculations below, showing all
Gas Law Stoichiometry Worksheet Name Period S+Udea+ Number Directions: Use significant figures and units in the problems below. ALL 1. Given the following unbalanced chemical equation for the combination reaction of sodium metal and chlorine gas: NaCl(s) Q Na(s) + a. What volume of chlorine gas, measured at STP, is necessary for the complete

Gas laws calculations worksheet
1. A gas has a volume of 800.0 mL at minus 23.00 °C and 300.0 torr. What would the volume of the gas be at 227.0 °C and 600.0 torr of pressure? 2. 500.0 liters of a gas are prepared at 700.0 mm Hg and 200.0 °C. The gas is placed into a tank under high pressure. When the tank cools to 20.0 °C, the pressure of the gas is 30.0 atm.
Taking a look at how to predict the behavior of gases, this quiz and corresponding worksheet will help you gauge your knowledge of calculating properties of a gas with the ideal gas law.
Gas Law Calculations Gas Law Calculations - Displaying top 8 worksheets found for this concept. Some of the worksheets for this concept are Gas laws work, Work 7, Gas laws practice calculations answer key, Chapters 10 11 gases gas laws and gas stoichiometry, Chapter8gasesandgasl, Honors unit 8 gas laws, Hvacr formulas, Supplemental activities.
Gas laws calculations worksheet.
Gas Law Worksheet #2 (Dalton's Law and Ideal Gas Law) Dalton's Law: P T = P 1 + P 2 + P 3 + . . . 1. Determine the total pressure of a gas mixture that contains oxygen at a pressure of 150.mmHg, nitrogen at 350.mmHg pressure, and helium at a pressure of 200.mmHg. 2. A gas mixture containing oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide has a ...
Mixed Gas Laws Worksheet - Solutions 1) How many moles of gas occupy 98 L at a pressure of 2.8 atmospheres and a temperature of 292 K? n = PV = (2.8 atm)(98 L) = 11 moles of gas RT (0.0821 L.atm/mol.K)(292 K) 2) If 5.0 moles of O 2 and 3.0 moles of N 2 are placed in a 30.0 L tank at a temperature of 25 ...
Worksheet 2.7: Stoichiometry Review GAS LAWS: Worksheet 3.1: Introduction to Gases & Dalton's Gas Law Worksheet 3.2: Boyles' Gas Law Worksheet 3.3: Charle's Gas Law Worksheet 3.4: Lusac's Gas Law Worksheet 3.5: Combined Gas Law Worksheet 3.6: Ideal Gas Law Worksheet 3.7: Gas Stoichiometry Worksheet 3.8: Review of Gases SOLUTIONS:
20) If I have 7.7 moles of gas at a pressure of 0.09 atm and at a temperature of 56 0C, what is the volume of the container that the gas is in? 21) If I have 17 moles of gas at a temperature of 67 0C, and a volume of 88.89 liters, what is the pressure of the gas? Avogadro's Law Problems: 1 mole = 22.4 L. 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 molecule. 1 mole ...
Assume the gas was at constant volume and the can did not explode. P 1 = P 2 = V 1 = V 2 = T 1 = T 2 = 6. A sample of hydrogen at 47 ºC exerts a pressure of 0.329 atm. The gas is heated to 77 ºC at a uniform volume. What will its new pressure be? P 1 = P 2 = V 1 = V 2 = T 1 = T 2 = 7. The volume of a gas at 27.0 ºC and 0.200 atm is 80.0 mL.
GAS LAW PROBLEMS 1. If a gas at occupies 2.60 liters at a pressure of 1.00 atm, what will be its volume at a pressure of 3.50 atm? 2. A gas occupies 900.0 mL at a temperature of 27.0 °C. What is the volume at 132.0 °C? 3. What change in volume results if 60.0 mL of gas is cooled from 33.0 °C to 5.00 °C? 4.
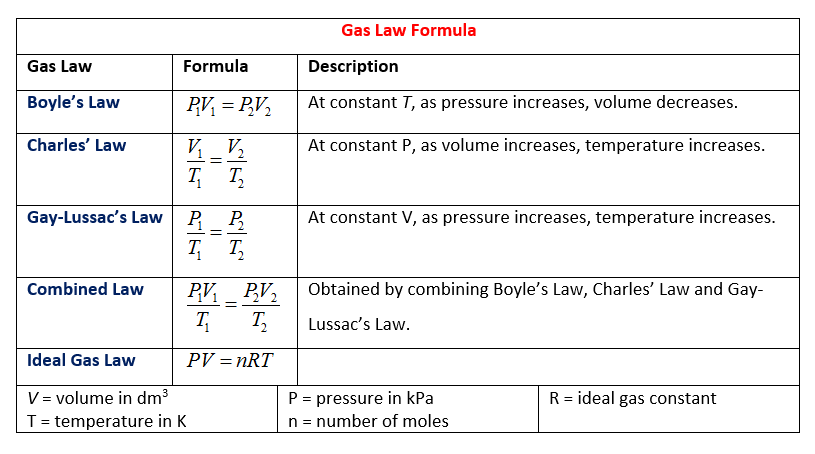
The gas laws are a group of laws that govern the behaviour of gases by providing relationships between the temperature, moles, volume and pressure associated with a gas. Learn about the 5 different gas laws and their formulae.
While we talk related with Gas Law Calculations Worksheets Answers, we've collected some variation of images to give you more ideas. chemistry gas laws worksheet, ideal gas law worksheet answers and ideal gas law worksheet answers are three of main things we will present to you based on the post title.
Gas Laws Quiz. This online quiz is intended to give you extra practice in performing a variety of gas laws calculations involving pressure, volume and temperature, as well as Ideal Gas Law problems. Select your preferences below and click 'Start' to give it a try! Number of problems: 1. 5.
Practice Ideal Gas Law Worksheet: 1 - 4 (page 12 in packet) Gas Stoichiometry Molar Volume - 1 mol of any gas at STP has a volume of 22.4 L 1 mol = conversion factor (only to be used at STP) 22.4 L canusemdarvolume Example: What is the mass of 98.0 ml of sulfur dioxide at STP? (work together on board - copy
Gas Laws Worksheet atm = 760.0 mm Hg = 101.3 kPa= 760 .0 torr Boyle's Law Problems: 1. If 22.5 L of nitrogen at 748 mm Hg are compressed to 725 mm Hg at constant temperature. What is the new volume? 2. A gas with a volume of 4.0L at a pressure of 205kPa is allowed to expand to a volume of 12.0L.
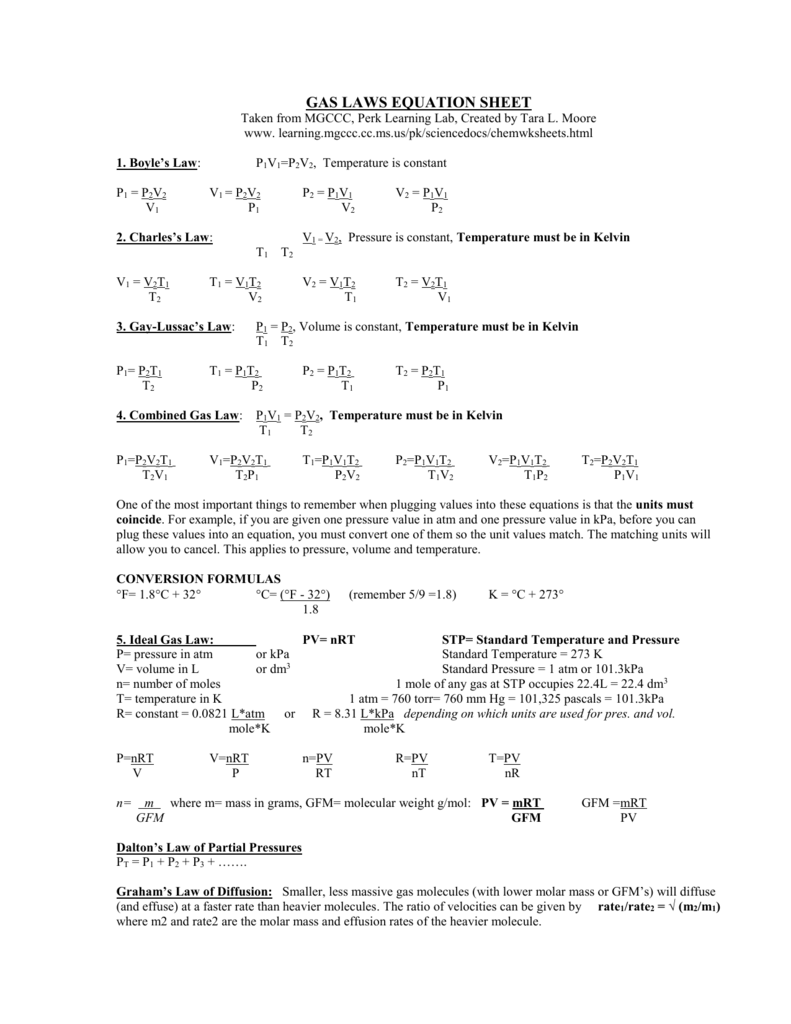
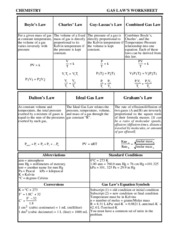
Worksheet 7 - Ideal Gas Law I. Ideal Gas Law The findings of 19th century chemists and physicists, among them Avogadro, Gay-Lussac, Boyle and Charles, are summarized in the Ideal Gas Law: PV = nRT P = pressure V = volume n= moles of gas, R = universal gas constant T = temperature. The value of R varies with the units chosen: R = 0.08206 L atm / mol K
Ideal Gas Law Metric and Imperial: P x V = (n x R) x T or PV = nRT Temperature, Volume and Pressure Calculations Calculating PO2 and PN2 Metric and Imperial: PO2 = P x FO2 and PN2 = P x FN2 Calculating FO2 and FN2 Metric and Imperial: FO2 = PO2 / P and FN2 = PN2 / P Calculating Max Depth of a Nitrox Mixture that does not Exceed a Specified PO2
Mr. Christopherson. G A S L A W S : Lesson Plans & Lecture Outlines. * Unit 10 Notes - Gas Laws pdf (25 pages) ( students) pdf. * Overhead - Transparencies pdf. * Gas Law Lessons pdf. * Gas: Main Points pdf. * Corwin Textbook - Publisher Website with Objectives and Quizzes. * Lesson Plans pdf.
Combine Gas Law Worksheet (DOC 24 KB) Density and Formula Mass Conversions of Ideal Gases (DOC 24 KB) Test Review - Gas Laws (DOC 38 KB) Weekly 12 Homework (DOC 91 KB) NEED HELP DOWNLOADING: doc file: You need the Microsoft Word program, a free Microsoft Word viewer, or a program that can import Word files in order to view this file.
is the ideal gas law constant, 8.3145 kg- m/kgmole-K . T. is the absolute temperature of the gas in K . With these units for . P, V, R, and T, the gas density will be in kg/m 3.. Critical Temperature and Pressure: As noted in the Introduction, in order to use the Ideal Gas Law to calculate a gas density, the gas temperature
Worksheets. Periodic Table Worksheet; Proton, Neutron and Electron Worksheet; Electron Configuration Worksheet; Elements Compounds Mixtures Worksheet; Calculations. Calorimetry Worksheet; Mixed Gas Laws Worksheet; Molar Mass Worksheet; Mole Calculations Worksheet 1; Mole Calculations Worksheet 2; Percent Composition Worksheet Nomenclature Handouts
View Gas+Laws+Calculations+WKST (4).docx from CHEMISTRY 1 CHEMISTR at Rossview High School. 6yjName: Gas Laws Worksheet #1 - Boyle's, Charles', and Gay-Lussac's Law Solve all problems - you
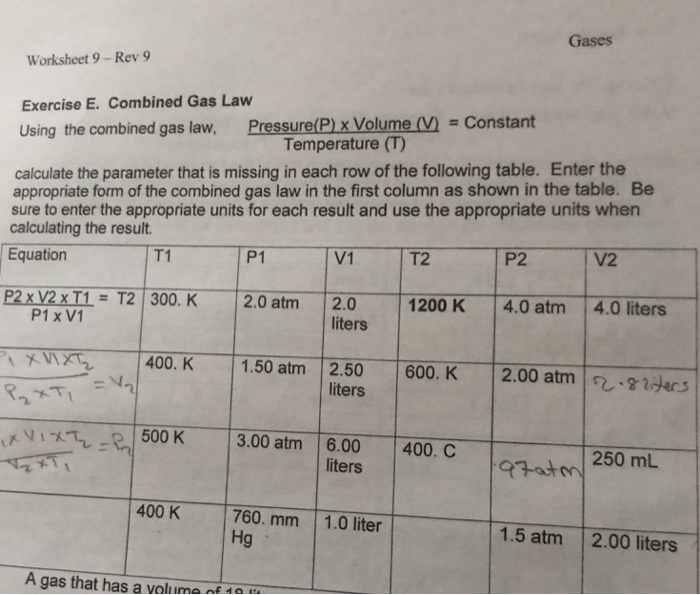
Combined Gas Law The combined gas law allows you to do calculations for situations in which only the amount of gas is constant. Example: The volume of a gas filled balloon is 30.0 L at 313 K and 153 kPa. What would the volume be at STP? PV= K P 1V 1 = P 2V 2 T T 1 T 2 Freddie Mercury
Avogadro's law: Equal volumes of different gases at the same pressure and temperature will contain equal numbers of particles. For example, if there are 2 moles of O. 2 in 50 cm3 of oxygen gas, then there will be 2 moles of N 2 in 50 cm3 of nitrogen gas and 2 moles of CO 2. in 50 cm3 of carbon dioxide gas at the same temperature and pressure.

Gas law practice problems: boyle's law, charles law, gay lussac's, combined gas law; crash chemistry
10. A sample of gas has a volume of 526 mL at 346 mmHg and 35(C. Determine the moles of gas. 11. Determine the pressure of 0.256 mole of neon gas in a 15.6 liter container at -35(C. 12. The pressure of a sample of carbon dioxide in a 1.85 liter container is 0.268 atm at 317K. Determine the mass of the gas and the density of the gas. 13.
General gas equation. The ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. This equation was first stated by French engineer and physist Emile Clapeyron (1799-1864) in 1834 as a combination of three empirical gas laws proposed by Robert Boyle, Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, and Amedeo Avogadro.
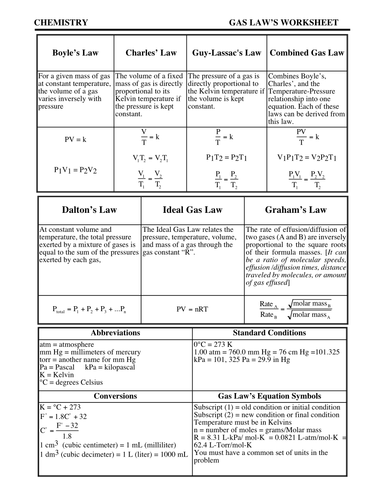
Charles’ Law For a given mass of gas at constant temperature, the volume of a gas varies inversely with pressure The Ideal Gas Law relates the pressure, temperature, volume, and mass of a gas through the gas constant “R”. Rate A Rate B = molar mass B molar mass A P total = P 1 +P 2 +P 3 +...P n PV = nRT The rate of effusion/diffusion of two gases (A and B) are inversely



























0 Response to "43 gas laws calculations worksheet"
Post a Comment