40 marbury v madison 1803 worksheet
Supreme Court Landmarks | United States Courts Marbury v. Madison (1803) Holding: Established the doctrine of judicial review. In the Judiciary Act of 1789, Congress gave the Supreme Court the authority to issue certain judicial writs. The Constitution did not give the Court this power. Landmark Supreme Court Cases | Cases - Gibbons v. Ogden This case explores the legal concepts of federalism, national supremacy, and the Commerce Clause.. In 1808, the government of New York granted a steamboat company a monopoly to operate its boats on the state’s waters, which included bodies of water that stretched between states.
Milestone Documents | National Archives Aug 03, 2022 · Marbury v. Madison (1803) Treaty of Ghent (1814) Expansion and Reform. Patent for Cotton Gin (1794) Jefferson's Secret Message to Congress Regarding the Lewis and ...

Marbury v madison 1803 worksheet
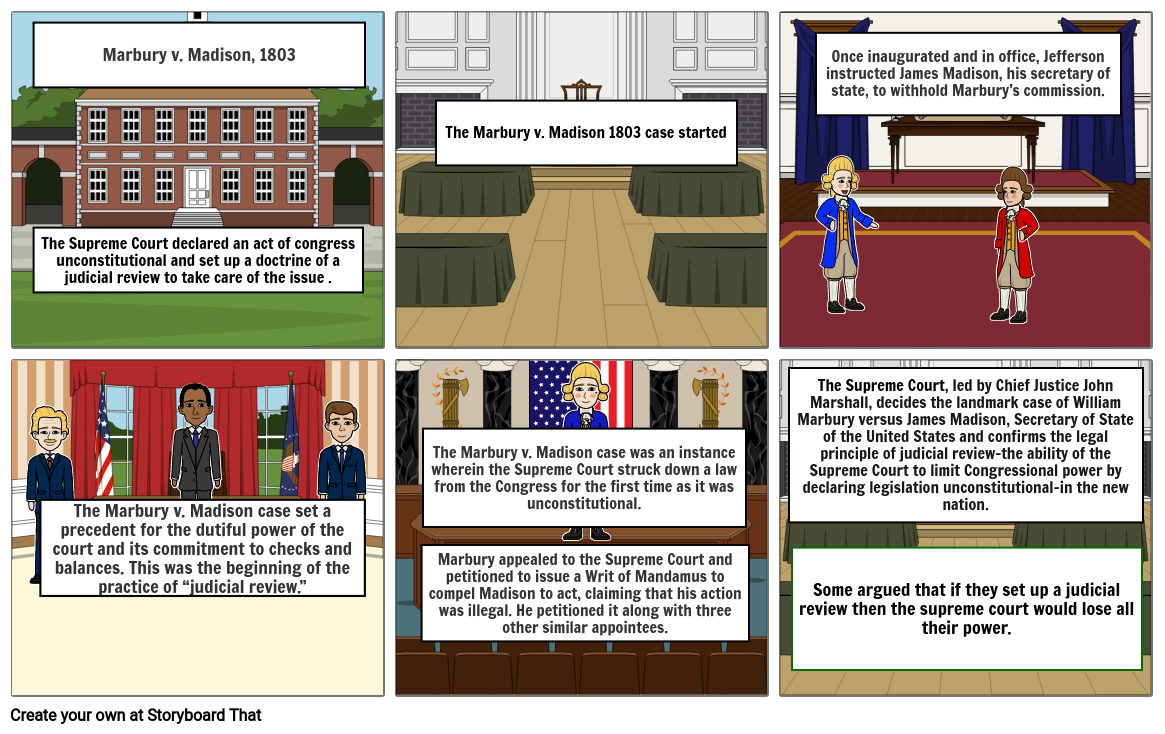
Landmark Supreme Court Cases | Cases - Marbury v. Madison At the end of President John Adams’ term, his secretary of state failed to deliver documents commissioning William Marbury as justice of the peace in the District of Columbia. Once President Thomas Jefferson was sworn in, he told James Madison, his secretary of state, not to deliver the documents to Marbury and others in order to keep members ... {{meta.fullTitle}} Unanimous decision for Marbury majority opinion by John Marshall. Though Marbury was entitled to it, the Court was unable to grant it because Section 13 of the Judiciary Act of 1789 conflicted with Article III Section 2 of the U.S. Constitution and was therefore null and void. Landmark United States Supreme Court Cases Marbury v. Madison (1803) Issue: Who can ultimately decide what the law is? Result: "It is explicitly the province and duty of the Judicial Department to say what the law is." Importance: This decision gave the Court the ability to strike down laws on the grounds that they are unconstitutional (a power called judicial review). McCulloch v.
Marbury v madison 1803 worksheet. Marbury v. Madison - Impact | Britannica Marshall’s masterful verdict has been widely hailed. In the face of attacks on the judiciary launched by Jefferson and his followers, Marshall needed to make a strong statement to maintain the status of the Supreme Court as the head of a coequal branch of government. By asserting the power to declare acts of Congress unconstitutional (which the court would not exercise again for more than ... Landmark United States Supreme Court Cases Marbury v. Madison (1803) Issue: Who can ultimately decide what the law is? Result: "It is explicitly the province and duty of the Judicial Department to say what the law is." Importance: This decision gave the Court the ability to strike down laws on the grounds that they are unconstitutional (a power called judicial review). McCulloch v. {{meta.fullTitle}} Unanimous decision for Marbury majority opinion by John Marshall. Though Marbury was entitled to it, the Court was unable to grant it because Section 13 of the Judiciary Act of 1789 conflicted with Article III Section 2 of the U.S. Constitution and was therefore null and void. Landmark Supreme Court Cases | Cases - Marbury v. Madison At the end of President John Adams’ term, his secretary of state failed to deliver documents commissioning William Marbury as justice of the peace in the District of Columbia. Once President Thomas Jefferson was sworn in, he told James Madison, his secretary of state, not to deliver the documents to Marbury and others in order to keep members ...































0 Response to "40 marbury v madison 1803 worksheet"
Post a Comment